Fine-tuning machine-learned particle-flow reconstruction for new detector geometries in future colliders
- This study demonstrates that a machine-learned algorithm for particle-flow reconstruction, when pre-trained on data from one particle detector, can be successfully fine-tuned for a different detector design to achieve the same performance as a model trained from scratch but with ten times less data.
- Phys. Rev. D 111, 092015 (2025)
- https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.111.092015
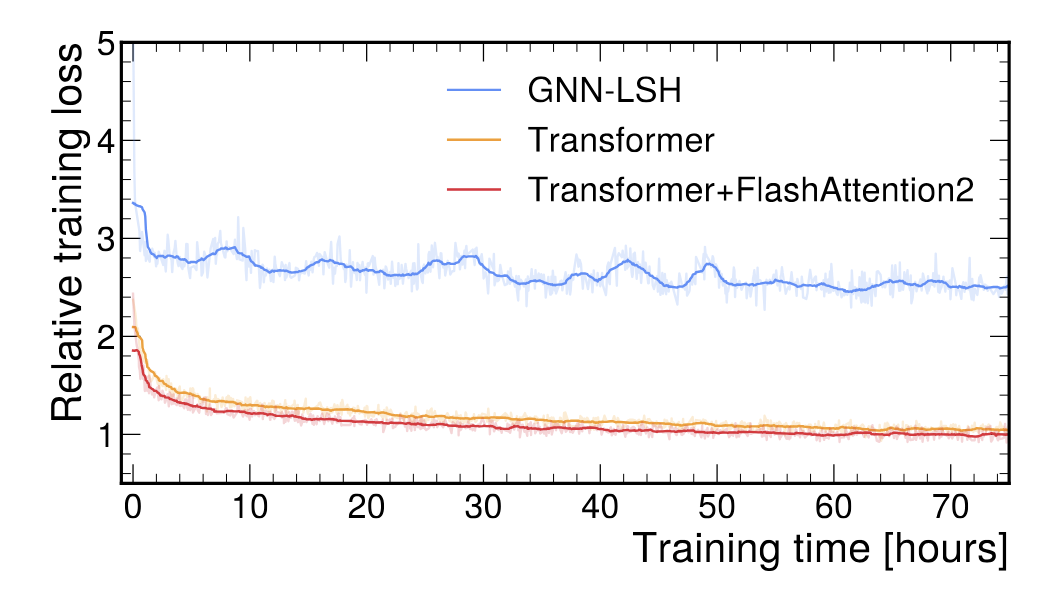
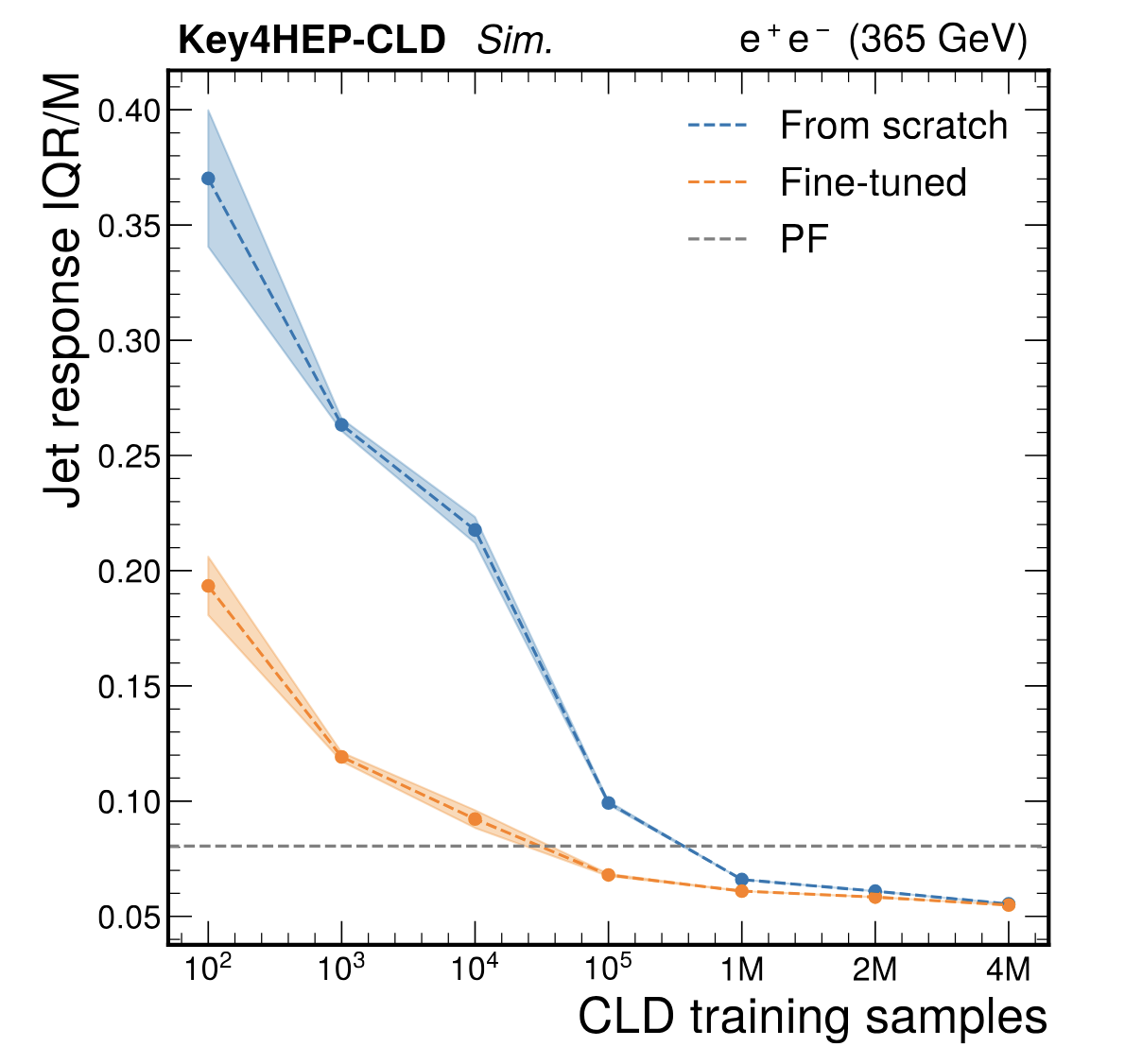 (Left) We find that using a transformer-based model improves the loss significantly compared to the previous graph neural network based model. (Right) Fine-tuning a pretrained model reduces the required dataset size by about 10x.
(Left) We find that using a transformer-based model improves the loss significantly compared to the previous graph neural network based model. (Right) Fine-tuning a pretrained model reduces the required dataset size by about 10x.
Reconstructing hadronically decaying tau leptons with a jet foundation model
- This paper investigates adapting the OmniJet-a jet foundation model, originally pretrained on a different dataset and task, to reconstruct hadronically decaying tau leptons, demonstrating that fine-tuning the pretrained model significantly improves performance, particularly momentum resolution, compared to training from scratch.
- SciPost Phys. Core 8, 046 (2025)
- https://doi.org/10.21468/SciPostPhysCore.8.3.046
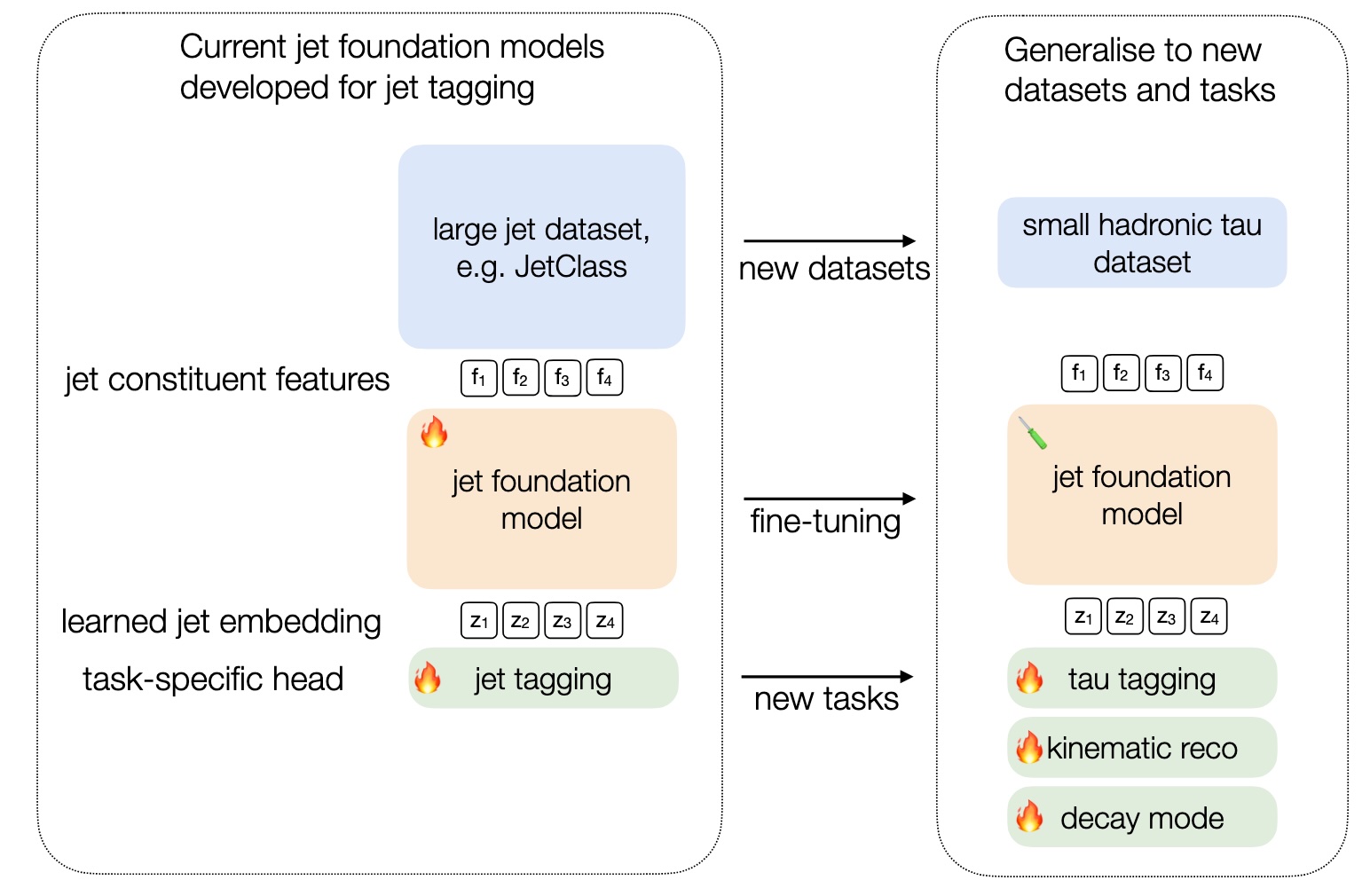
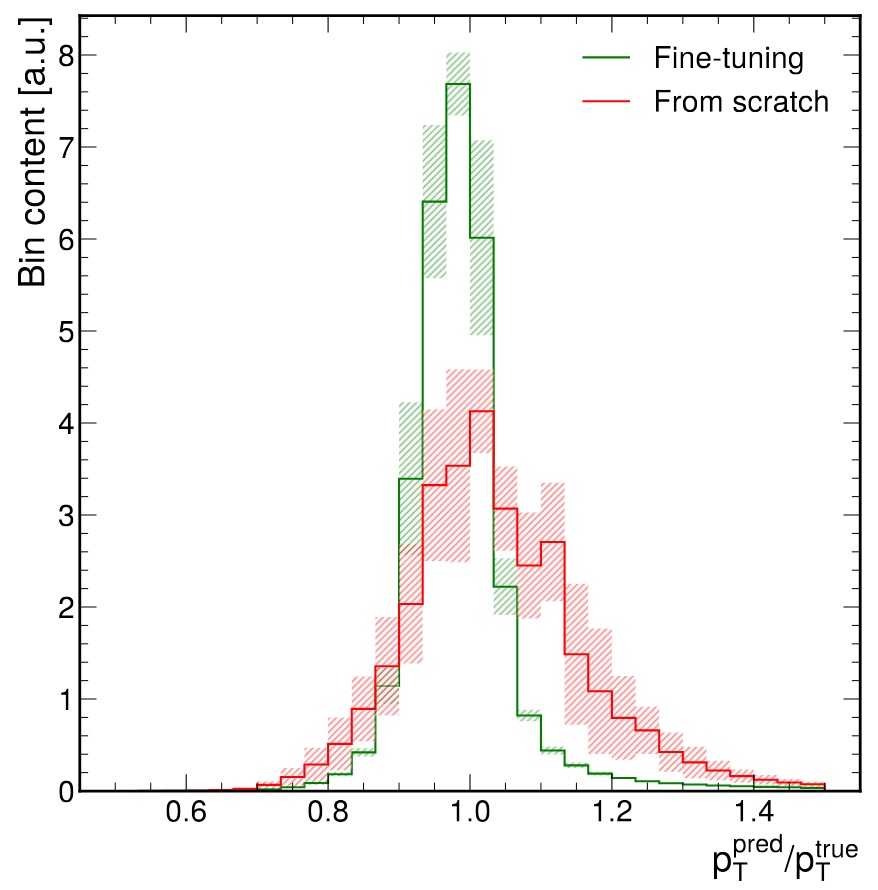 (Left) We contrast the typical training workflow for jet foundation models with the generalized approach used in this study to adapt an existing model to new datasets and tasks, specifically for hadronic tau lepton reconstruction. (Right) Fine-tuning improves the pT reconstruction resolution by approximately 50% compared to training from scratch on small datasets.
(Left) We contrast the typical training workflow for jet foundation models with the generalized approach used in this study to adapt an existing model to new datasets and tasks, specifically for hadronic tau lepton reconstruction. (Right) Fine-tuning improves the pT reconstruction resolution by approximately 50% compared to training from scratch on small datasets.
On the detection of stellar wakes in the Milky Way: a deep learning approach
- This paper assesses the viability of using deep learning trained on simulations to detect stellar wakes induced by dark matter subhalos in the Milky Way’s stellar halo, finding the method can infer subhalo presence down to masses of 5x10⁷ M☉.
- Astronomy and Astrophysics 693, A227 (2025)
- https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202451480
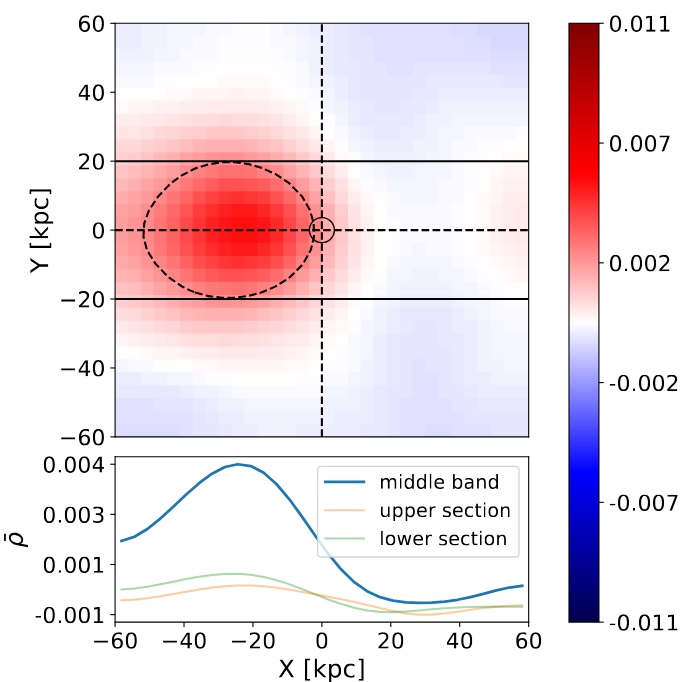
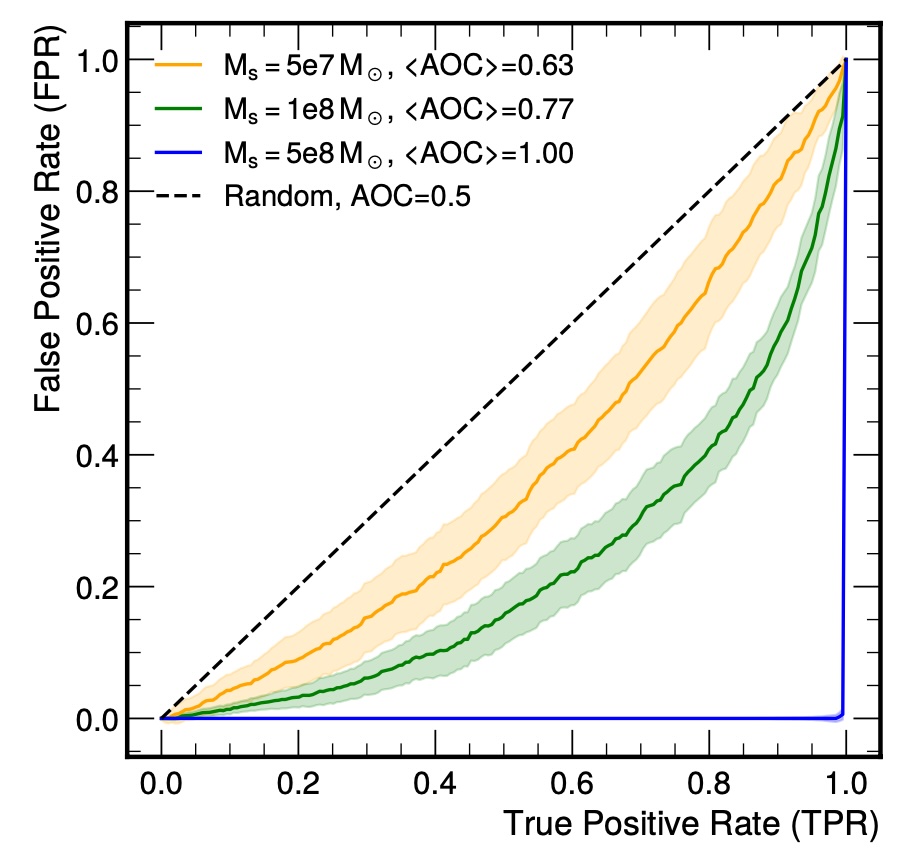 (Left) Simulated stellar overdensity wake induced by a 5x10⁸ M☉ subhalo moving through the stellar halo, projected onto the X-Y plane. (Right) This chart shows how well a machine learning model can find stellar wakes of different mass. A line closer to the bottom-right corner means the model is better at finding the wakes without mistakenly identifying random patterns as wakes.
(Left) Simulated stellar overdensity wake induced by a 5x10⁸ M☉ subhalo moving through the stellar halo, projected onto the X-Y plane. (Right) This chart shows how well a machine learning model can find stellar wakes of different mass. A line closer to the bottom-right corner means the model is better at finding the wakes without mistakenly identifying random patterns as wakes.
A unified machine learning approach for reconstructing hadronically decaying tau leptons
- Computer Physics Communications 307 (2025)
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2024.109399
- We show that tau leptons can be efficiently and accurately reconstructed using a multi-task machine learning setup.
Improved particle-flow event reconstruction with scalable neural networks for current and future particle detectors
- Nature Communications Physics 7, 124 (2024)
- https://doi.org/10.1038/s42005-024-01599-5
- We show that a scalable and portable graph neural network algorithm can efficiently reconstruct stable particles, resulting in more accurate event reconstruction.
Tau lepton identification and reconstruction: A new frontier for jet-tagging ML algorithms
- Computer Physics Communications 298 (2024)
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2024.109095
- We demonstrate that the transformer-based architecture can be used for tau lepton identification, and that it outperforms alternative approaches based on heuristic algorithms and convolutional nets.
A Bayesian estimation of the Milky Way’s circular velocity curve using Gaia DR3
- Astronomy and Astrophysics, Volume 676 (2023)
- https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202346474
- We analyzed large astrophysical datasets to accurately measure the rotation curve of the Milky Way Galaxy.
Sensitivity Estimation for Dark Matter Subhalos in Synthetic Gaia DR2 using Deep Learning
- Astronomy and Computing, Volume 41 (2022)
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ascom.2022.100667
- We applied deep learning based anomaly detection methods to search for rare astrophysical phenomena.
MLPF: Efficient machine-learned particle-flow reconstruction using graph neural networks
- European Physical Journal C, Volume 81 (2021)
- https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-021-09158-w
- We developed a novel graph neural network based particle flow reconstruction algorithm.
Data Analysis with GPU-Accelerated Kernels
- Proceedings of Science, Volume 390, ICHEP (2020)
- https://doi.org/10.22323/1.390.0908
- I developed a novel approach for large-scale high-energy physics data analysis based on GPUs, accelerating the time-to-insight by ~10x.
Observation of ttH production
- Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 231801 (2018)
- https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.231801
- I developed sensitive matrix-element based statistical analysis tools for the CMS observation.
Identification of heavy-flavour jets with the CMS detector in pp collisions at 13 TeV
- Journal of Instrumentation, Volume 13 (2018)
- https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-0221/13/05/P05011
- I developed a novel b-quark identification model (cMVAv2) based on xgboost, thus introducing industry-standard tools to the CMS b-tagging team.